joinStrings
Joins a set of strings or lists to create a single string.
The function is often combined with map to produce an amended list of values.
Parameters
STRING (string or list)
The first string or list to join.
STRING (string or list)
The second string or list to join. You can add more strings or lists if required.
Examples
These examples show how to join strings:
ATL in Script | Result |
|---|---|
| ABC |
| BrianBlessed |
| Brian Blessed |
| Brian Blessed |
These examples show the effect when you join lists:
ATL in Script | Result |
|---|---|
| ABCDEF |
| ABCDEF |
Tip
The result is a concatenated string. To flatten a list of lists into a one list, use flattenLists.
Using joinStrings with map
The function is often combined with map to produce an amended list of values.
ATL in Script | Result |
|---|---|
[[ myList = makeList(10,20,30) map(myList, x -> joinStrings(x,'%')) ]] | 10%, 20% and 30% |
[[
myList = makeList('week','month','year')
map(myList, x -> joinStrings(x,'ly'))
]] | weekly, monthly and yearly |
Complex example
The joinStrings and map combination is helpful when mapping a complex list-like structure such as a list of ATL objects.
Important
Download and open THIS EXAMPLE PROJECT to work through the next example.
Go to the project's SummaryNarrative script and click Preview. You should see this:
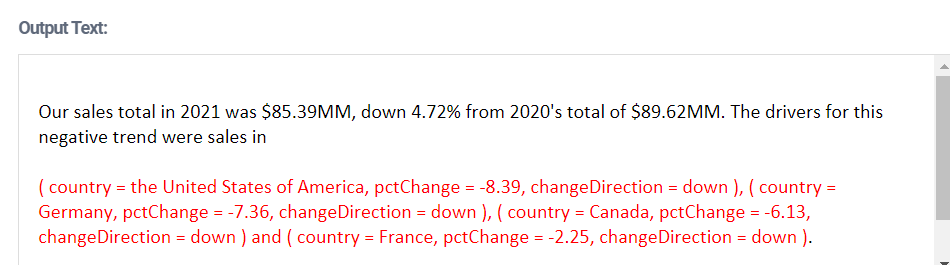
The content in red is a list of ATL objects: one object for each driver country. Each object has three fields: country, pctChange, and changeDirection. We want to map the list of objects to this list of strings:
the United States of America (8.39% down), Germany (7.36% down), Canada (6.13% down) and France (2.25% down).
Change the last ATL block to:
[[map(driverAnalytics(data2021,data2020), x -> x.country)]].
Click Preview. You should see this:
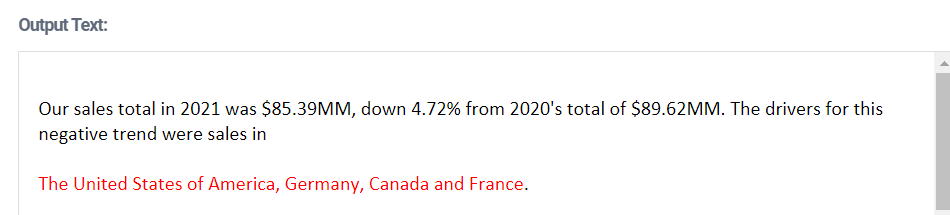
Using
mapand dot notation, we've mapped the list of ATL objects to a list of countries, but we needjoinStringsto pull in other values from each ATL object. We can also add parentheses where required.Change
[[map(driverAnalytics(data2021,data2020), x -> x.country)]]to:[[map(driverAnalytics(data2021,data2020), x -> joinStrings(x.country," (", abs(x.pctChange), "% ", x.changeDirection,")"))]]Note
Note that quotation marks aren't required for parameter inputs such as
x.countryorabs(x.pctChange)— as these return a string or numeric value — but quotation marks are required for the other input strings.Join the ATL block to the end of the preceding paragraph, select all script content, and click Clear Formatting:
Click Preview. You should get this narrative output:
Our sales total in 2021 was $85.39MM, down 4.72% from 2020's total of $89.62MM. The drivers for this negative trend were sales in the United States of America (8.39% down), Germany (7.36% down), Canada (6.13% down) and France (2.25% down).